

We will learn about the fundamentals of OOPs on this page. The
paradigm of object-oriented programming offers several ideas,
including polymorphism, inheritance, and data binding.
Object-Oriented
Programming, or OOPs, refers to programming languages that employ
objects as a key source for implementing
what is to happen in the code.
The user or viewer see objects as they execute the tasks
assigned to them. They apply real-world principles such as
inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and other relevant
concepts.
in programming is the goal of object-oriented programming.
OOP's primary goal is to bind together the data and the method that use them so that only that function and no other part of the code can access the data. The first programming language that was genuinely object-oriented is smalltalk.
1. Class
2. Object
3. Method
4. Pillars of OOPs
In addition to these concepts, there are a few other terms used in Object-Oriented design:
1. Association
2. Aggregation
3. Cohesion
4. Coupling
5. Composition
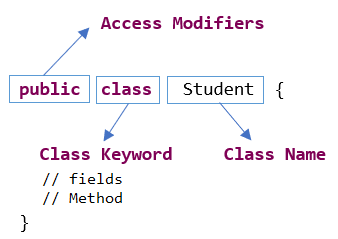

// Java program using class and object
public class Student{ static String Student_name; static int Student_id; static void set(String name, int id) { Student_name = name; Student_id = id; } static void get() { System.out.println("Student name is: " +Student_name ); System.out.println("Student id is: " + Student_id); } public static void main(String args[]) { Student.set("Dr Alok Raja", 1403195); Student.get(); } }
Output:
Student name is: Dr Alok Raja
Student id is:14031952
Difference Between Object-Oriented and Procedure Programming languages are mention below
| S.N | Procedural Programming | Object-Oriented Programming |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A programming paradigm known as procedural programming centres the program's structure around procedures or functions. It separates the programme into smaller modules or functions and focuses on providing step-by-step instructions to solve a problem. | The basic concept of the object-oriented programming (OOP) is the interaction of objects.The division of data and tasks into reusable "objects" that can communicate and share resources is highlighted. |
| 2. | The focus of procedural programming is on breaking down the issue into a series of steps or procedures. It follow Top-down approach, the main programme calling various functions to carry out the desired task. | The focus of object-oriented programming(OOP) is to making objects that can interact and work together to solve problems by encapsulating data and methods. OOP follow a bottom-up methodology in which objects are created and modified to produce the desired results. |
| 3. | Procedural programming is insecure compared to object-oriented programming(OOPs). | Object-oriented programming(OOPs) uses abstraction to achieve data hiding. As a result, it provides greater security than procedural programming. |
| 4. | Procedural programming organizes data and code into separate functions or modules. Data is typically stored in global variables, accessible by multiple function i.e Data moves freely within the system from one function to another function in procedural programming. | Object-oriented programming organizes data and code into classes and objects. Data is encapsulated within objects, and functions associated with objects are called methods. Objects can interact with each other through method invocations and exchange data using member variables. |
| 5. | There are no access modifiers in procedural programming, | private, public, and protected are access modifiers in Object-oriented programming(Oops) |
| 6. | Code reusability in procedural programming is achieved buy use of functions. Functions can be called from different parts of the program, allowing code to be reused. | Object-oriented programming promotes code reusability using the concept of inheritance. Classes can inherit properties and behaviors from other classes.In this way code is reused. |
| 7. | Method Overloading is not possible in procedural programming language. | Method overloading or method overriding is possible in Object-oriented programming |
| 8. | No concept of Abstraction(Data Hiding) or Inheritance in procedural programming. | The Abstraction(Data Hiding) or Inheritance are main pillar of O bject-oriented programming. |
| 9. | In procedural programming, error handling is typically done through error codes or return values. | In object-oriented programming, exceptions are mainly used to handle errors, it make code more robust to handle error. |
| 10. | C, Fortran, Pascal, and Visual Basic are all examples of procedural programming. | Object-oriented programming examples include:.NET, C#, Python, Java, VB.NET, and C++. |
Post your comment