

// Java program using class and object
class Car { public int gear = 2; // state public void braking() // behavior { System.out.println("Car braks Working"); } }
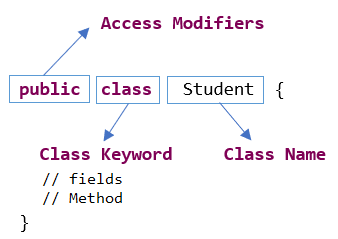
// Java program using class and object
class Student2{ String Stu_name ; int Stu_id; void insert(String stu_name, int stu_id) { Stu_name = stu_name; Stu_id = stu_id; } public void Display() { System.out.println(Stu_id); System.out.println(Stu_name+"\n"); } } class Student{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 studentObject1=new Student2(); Student2 studentObject2=new Student2(); studentObject1.insert("Dr Alok Raja ", 40139522); studentObject1.Display(); studentObject2.insert("Mrs Anita Sinha", 40139522); studentObject2.Display(); } }
Output:
40139522
Dr Alok Raja
40139532
Mrs Anita Sinha
Difference between object and class are mention below
| S.N | Object | Class |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | An Objects are instances of classes. | An outline or model for creating new objects is called a class. |
| 2. | A real-world item is an object, such as a car,bike,table,fan, etc. | A class is a collection of similar object. |
| 3. | Physical entity are called objects. | A logical entity is a class. |
| 4. | Mainly the new keyword is used to create objects, as in Main main=new Main (); | The class keyword is used to declare classes, such as class Main{} |
| 5. | Depending on the need, an object is created multiple times. | Classes are only declared once. |
| 6. | Memory is allocated whenever an object is created. | There is no memory allotted when a class is created. |
| 7. | The new keyword, newInstance() method, clone() method, factory method, and deserialization are just a few of the ways to create an object in Java. | In Java, the class keyword is the only way to define a class. |
Police Colony
Patna, Bihar
India
Email:
Post your comment